

Rainforest Deforestation
- What is Deforestation?
- Causes Of Deforestation
- Effects of Deforestation
- Deforestation and Climate Change
- Are there government subsidies for reforestation?
What is Deforestation?
Deforestation is the permanent destruction of rainforests to make land available for non-forest uses. An estimated 18 million acres (7.3 million hectares) of forest, an area about the size of panama, is deforested each year; according to the United Nations Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO).
View photos of deforestation in areas where Community Carbon Trees plants:

Causes Of Deforestation
Major causes of deforestation:
- Large cattle operations by multinational agribusiness
- Monocrop agriculture, such as palm oil plantations, teak plantations, unsustainable coffee farms, pineapple farms, and cacao farms
- Large, intensive real estate developments
- Population growth
Not all deforestation is intentional. Sometimes deforestation is caused by a combination of human and natural factors like wildfires and overgrazing. In addition, the edges of existing forest are vulnerable to deterioration by wind and rain and natural effect of erosion.
Deforestation in Costa Rica began in 1970 when cattle farmers were subsidized by first world countries to burn forests in order to provide a cheap source of meat to multi-national companies Burger King and Wendy's. For the past 20 years, Costa Rica has been deforested by locals and foreigners who are converting forests into monocrop agricultures and real estate developments. This is an ongoing problem.
It is generally accepted that the world's population is increasing by about 1 billion people every decade. The United Nations Population Division predicts that our numbers will reach 8.9 billion people by 2050, with the greatest growth in the tropics. We can expect the rate of deforestation to increase as competition for food, land, and resources increases. The need to create sustainable systems of economics and food now is important for addressing foreseeable problems in the future.
Effects of Deforestation
The effects and consequences of deforestation are local and global:
- Desertification
- Species extinction
- Biodiversity loss
- Hydrological Cycle Disruptions
- Sediments in water kill fisheries and smother coral reefs
- Stormwater runoff of pesticides and herbicides into rivers, estuaries and oceans
- Watershed flooding
- Drought
- Loss of local water supplies
- Rise in temperatures
- Breakdown of indigenous communities

Rainforest deforestation is a physical, chemical, and biological process set in motion when the protective cover of vegetation is removed and the land is subjected to intense tropical sun and torrential rains.
Deforestation effects include accelerated erosion, leaching, soil compaction, decreased soil fertility, diminished natural plant regeneration, interruption of hydrological cycles, water salinization, waterlogging, flooding, increased drought risk, and the establishment of undesirable weedy plants. There is a strong relationship between inappropriate land-use practices and land degradation. Often the combination of low soil fertility and infestation of weeds leads to land abandonment.
Deforested areas in North Africa have now become deserts. Today, huge dust storms of noxious particulates spread across the globe creating a strange haze in the atmosphere. This further increasing the greenhouse effect.
The effects of deforestation can be catastrophic for all the creatures and insects that rely on the forest for food, habitat, and migration. The chain of being is only as strong as its weakest link, and when forests are indiscriminately altered, whole ecosystems can be seriously affected.
Costa Rica is an important feeding ground for birds. Canada has 160 bird species spread over a huge landmass, while the tiny country of Costa Rica has over 850 species. This is because a large percentage of birds from North and South America migrate to Costa Rica to feed and strengthen themselves before flying home. When food supplies here are insufficient bird populations throughout North and South America suffer. This in turn creates detrimental effects on the control of insects and insect-borne diseases throughout the whole continental landmass.


Deforestation in mountainous regions is one of the most serious ecological problems today. Disturbance of vegetative cover on mountain areas creates thin soil and steep slopes resulting in land instability, landslides, and soil erosion. Roads and homesites that are poorly cut into hillsides and unsupported by vegetation inevitably slide. This adds tons of dirt to stormwater runoff and pollutes rivers. Rivers turn brown after a strong rain and carry huge amounts of sediments to the ocean. This devastates freshwater and coastal fisheries, in addition to smothering coral reefs and polluting whale breeding areas. Studies of plankton off the Pacific coast show signs of mortality loss caused by continuous years of elevated ocean temperatures.
The utter devastation which occurred in Honduras and surrounding countries as a result of Hurricane Mitch in 1998 shows the long-term catastrophic consequences of deforestation. Every rainy season in Costa Rica features a new onslaught of natural disasters largely caused by deforestation and inappropriate land use. Read more about risks to newly planted trees.



When rivers and natural water springs are covered by healthy forest, ecosystems are protected from hot tropical sun rays. Trees and vegetation hold rainwater in the soil like a sponge and prevent it from running swiftly over the surface of the land. Without trees and surface vegetation slowing and moving the rain deep into the earth, many underground aquifers, springs and creeks are in danger of drying up. The loss of water affects local communities that depend on water for irrigation in the dry season and the necessities of daily life. Recent development and construction has put even more pressure on local water supplies, storage systems, and infrastructure that were not designed to handle such high demand.
Deforestation also deals long-term blows to indigenous communities. For them, the arrival of "civilization" usually means the destruction of traditional lifestyle and the breakdown of social institutions. On the other hand, reforestation of suitable land provides local populations opportunities to work in partnership for a better and more sustainable way of life. Local Costa Ricans (Ticos) can maintain their cultural ways of life and take great pride in replacing what was cut down by their predecessors.
Deforestation and Climate Change
The link between deforestation and climate change is known.
Climate change is the biggest problem facing our planet. preserving our remaining forests is a key part of the solution. Deforestation and forest fires contribute approximately 25% of total carbon dioxide emissions.
"Action to preserve the remaining areas of natural forest is needed urgently," The Stern Review on the Economics of Climate Change (2006). Preventing deforestation would be a relatively cheap method of tackling climate change, allowing forested countries to reduce their emissions by enormous amounts and benefiting the entire planet. There is growing acceptance among the international community for financial incentives to leave forests standing. If that were to happen, forests could be worth more intact than if they were cut for timber and agriculture.
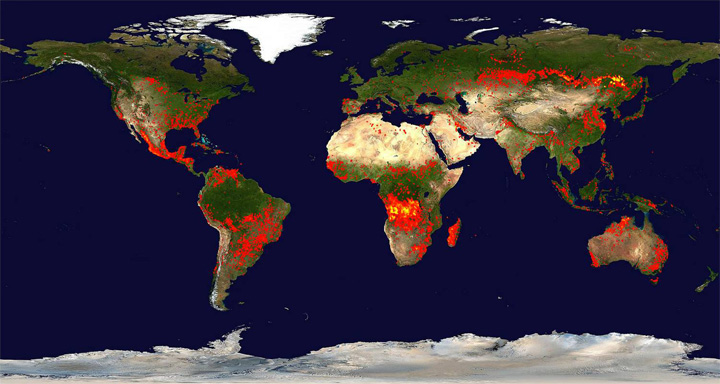
Day and night satellite images of heat from deforestation.
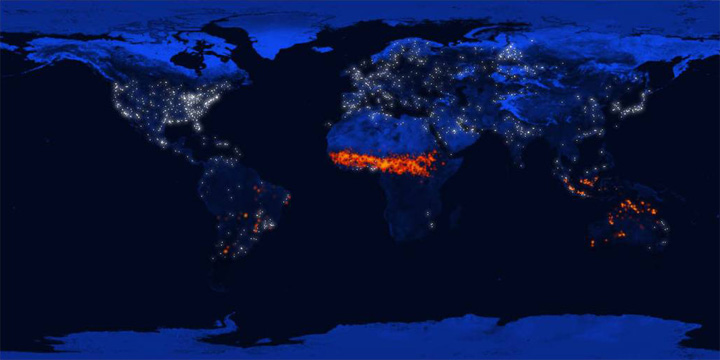
The heart of the African continent has suffered an accelerated process of deforestation since the 60's. Territories of countries like Libia, Chad, Nigeria, Mali, Benin y Camerun have gradually been turned into desert.
Are there government subsidies for reforestation?
Today, local farmers earn more from agricultural activities like growing pineapple and bananas, and even African Oil Palms, rather than conserving forests. Clearing their land of trees to make available agricultural space for profitable crops is more economically feasible. The money which can be obtained for tropical rare hardwoods also tempts many locals to cut huge, rare trees, illegally.
Read more about the value of trees and value of land for agriculture in Costa Rica.





